Superheterodyne Receivers
Course Introduction: Dissecting Superheterodyne Receiver Components
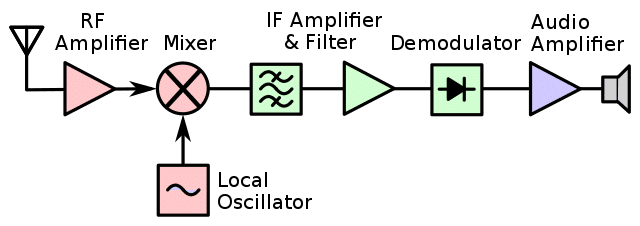
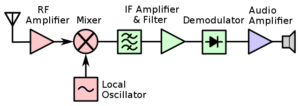
This chapter provides an overview of the critical components in superheterodyne receivers by explaining the answers to 11 key questions. The course starts by exploring the mixer stage’s role in frequency conversion (Question A-006-002-001), demonstrating how it changes the incoming signal to the Intermediate Frequency (IF). Learners will understand the necessity of the Beat-Frequency Oscillator (BFO) in Single Sideband (SSB) reception (Question A-006-002-002) and delve into the functionality of the first mixer in producing the IF (Question A-006-002-003). The course also addresses practical scenarios, such as calculating the local oscillator frequency for precise signal reception (Question A-006-002-004).
Further, the course examines the offset function of the BFO relative to the incoming signal for effective SSB signal detection (Question A-006-002-005) and emphasizes the importance of oscillator stability and spectral purity in superheterodyne receivers (Question A-006-002-006). Tuning mechanisms, critical for aligning the local oscillator and ensuring accurate frequency reception, are discussed (Questions A-006-002-007 and A-006-002-008). Additionally, the process of combining signals in the mixer stage to produce the IF is explored (Question A-006-002-009), alongside an examination of which receiver stages have input circuits tuned to the same frequency for optimal mixing and selectivity (Question A-006-002-010). The chapter concludes by reiterating the primary function of the mixer stage in generating the IF (Question A-006-002-011), consolidating learners’ understanding of these fundamental concepts in radio technology.