Start Here
AM, Single Sideband, and Linearity in Transmitters
This chapter delves into the complex world of amplitude modulation (AM) and single sideband (SSB) transmission, focusing on the technical nuances that ensure high-quality signal transmission in radio communication. We begin by exploring the function of balanced modulators in generating double sideband signals with suppressed carriers, a critical step in SSB transmission. The chapter then examines the processes for producing single-sideband signals and the importance of carrier suppression for efficient transmission. Special attention is given to the concept of linearity in transmitters, particularly in SSB, where signal integrity is paramount. The two-tone test, a standard method for assessing transmitter linearity, is discussed in detail, highlighting its significance in ensuring that the transmitter can accurately process complex audio signals. The phenomena of “flat-topping” and its implications for signal quality are also explored. Through this chapter, readers gain a comprehensive understanding of the technical aspects that govern AM and SSB transmissions, emphasizing the importance of precision and control in modern radio communication systems.
Be sure to login to your hamshack.ca account to track your progress by clicking the [Mark Complete] Button at the bottom of each lesson. You can contact VE7DXE to sign-up for the new Basic Amateur course.
Balanced Modulator and Double Sideband Signals (A-005-004-001)
Creating DSB Signals in Modulators: In Question A-005-004-001, the function of a balanced modulator is examined. The correct answer, A. Double sideband, suppressed carrier, reveals that a balanced modulator generates a double sideband signal where both the upper and lower sidebands are present, but the carrier is absent. This type of signal is crucial in certain communication systems, like Single Sideband (SSB) transmissions, where carrier suppression improves efficiency. The balanced modulator achieves this by mixing (or modulating) an audio signal with a carrier frequency in such a way that the carrier is canceled out, leaving only the sidebands. This process is akin to a chef blending ingredients to create a new dish where the original flavors are transformed into something new and more efficient.
Parallels:
- Mixing Paints: Like mixing blue and yellow paint to get green, a balanced modulator combines audio and carrier signals to produce sidebands.
- Creating a Blend in Cooking: Similar to how a chef combines ingredients to create a dish where individual flavors are transformed, the modulator blends signals to form a DSB signal.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- Double Sideband Output: Produces signals with both upper and lower sidebands.
- Suppressed Carrier: Eliminates the carrier frequency.
- Efficiency in Communications: Useful in systems like SSB for improved transmission efficiency.
- Signal Transformation: Alters the original signal to a more useful form.
- Crucial in RF Modulation: Represents a fundamental technique in radio communication.
Producing Single-Sideband Phone Signals (A-005-004-002)
SSB Signal Generation Process: Question A-005-004-002 addresses how to produce a single-sideband phone signal. The answer, D. By using a balanced modulator followed by a filter, indicates the two-step process involved. First, a balanced modulator creates a double sideband signal with a suppressed carrier. Then, a filter is used to remove one of the sidebands (either upper or lower), leaving only the desired single sideband for transmission. This process is important in SSB communications, where removing one sideband and the carrier significantly improves power efficiency and bandwidth usage. It’s like a sculptor who first carves a rough shape (DSB signal) and then chisels away unnecessary parts to reveal the final sculpture (SSB signal).
Parallels:
- Art of Sculpting: Similar to sculpting where unnecessary material is removed to reveal the final shape, the filter in SSB removes the undesired sideband.
- Editing a Document: Like editing a document to keep only essential information, the filter process trims the DSB signal to retain just the required sideband.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- Two-Step Signal Creation: Involves both modulation and filtering.
- Balanced Modulator Role: Generates the initial DSB signal.
- Filtering Process: Removes one sideband, leaving the SSB signal.
- Efficiency and Bandwidth Utilization: SSB is more power-efficient and uses bandwidth more effectively.
- Key in Modern Communication Systems: Demonstrates an advanced technique in radio transmissions.
Carrier Suppression in SSB Transmitters (A-005-004-003)
Role of the Balanced Modulator in SSB: Question A-005-004-003 delves into where carrier suppression occurs in a single-sideband (SSB) transmitter. The answer, A. the balanced modulator stage, points out that this critical function is primarily executed in the balanced modulator. This stage effectively cancels out the carrier frequency, leaving only the sidebands. Carrier suppression in SSB is essential for reducing power waste and increasing the efficiency of the transmission, as the power that would otherwise be used for the carrier is instead utilized for the sidebands, carrying the actual information.
Parallels:
- Filtering Coffee: Just as a coffee filter removes grounds, leaving behind the drinkable coffee, the balanced modulator filters out the carrier, leaving the useful sidebands.
- Sculpting from Marble: Similar to a sculptor removing excess marble to reveal the statue, the modulator stage suppresses the carrier to reveal the pure sideband signal.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- Carrier Suppression Mechanism: Occurs in the balanced modulator.
- Increases Transmission Efficiency: More power is devoted to the sidebands.
- Essential in SSB Transmitters: A fundamental aspect of SSB technology.
- Reduces Power Waste: Eliminates unnecessary carrier transmission.
- Technical Innovation in RF Communication: Demonstrates a sophisticated approach to signal processing.
SSB vs. AM Transmission (A-005-004-004)
Benefits of SSB Over Conventional AM: In Question A-005-004-004, the comparison between single-sideband (SSB) and conventional amplitude modulation (AM) transmission is addressed. The answer, D. 6 dB gain in the transmitter and 3 dB gain in the receiver, signifies the efficiency advantages of SSB. In SSB, the elimination of one sideband and the carrier translates to a 6 dB reduction in power requirements for the transmitter and a 3 dB improvement in the signal-to-noise ratio at the receiver. This makes SSB more power-efficient and effective in terms of signal clarity over long distances compared to traditional AM, which transmits the carrier and both sidebands.
Parallels:
- Fuel Efficiency in Cars: Like a fuel-efficient car that goes farther on less fuel, SSB achieves more with less power compared to AM.
- Eco-Friendly Light Bulbs: Similar to how LED bulbs provide more light with less energy than incandescent bulbs, SSB transmits clearer signals using less power.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- Power Efficiency: SSB is more power-efficient than AM.
- Improved Signal Clarity: Offers a better signal-to-noise ratio at the receiver.
- Reduction in Power Needs: Saves energy for the transmitter.
- Effective Long-Distance Communication: Ideal for reaching far distances with clarity.
- Advancement in Transmission Technology: Demonstrates a more sophisticated approach to radio broadcasting.
Two-Tone Test in SSB Transmitters (A-005-004-005)
Peak Power in Two-Tone Testing: Question A-005-004-005 explores the peak power output measurement of a single-sideband (SSB) transmitter when tested with a two-tone generator. The correct answer, D. twice the RF power output of any of the tones, indicates that the peak power output in this scenario is double the RF power of either tone. In a two-tone test, two audio-frequency tones are simultaneously transmitted, and their combined peak power is crucial for evaluating the transmitter’s linearity and performance. This test ensures that the transmitter can handle simultaneous multiple frequencies without distortion, a key aspect of SSB transmission quality.
Parallels:
- Blending Musical Notes: Like playing two notes together on a piano louder than a single note, the combined power in a two-tone test is greater than that of individual tones.
- Combining Ingredients in Cooking: Similar to flavors intensifying when ingredients are mixed, the two-tone test combines tones for a heightened output measurement.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- Peak Power Measurement: Peak output is double that of individual tones.
- Evaluates Transmitter Performance: Assesses linearity and handling of multiple frequencies.
- Key in SSB Transmission Quality: Ensures transmission fidelity and efficiency.
- Test for Simultaneous Frequencies: Checks for distortion with multiple audio tones.
- Critical for Broadcast Reliability: Integral part of transmitter testing and maintenance.
Testing Amplitude Linearity in SSB Transmitters (A-005-004-006 &
Testing Amplitude Linearity in SSB Transmitters (A-005-004-006)
Amplitude Linearity with Two-Tone Signal: Question A-005-004-006 asks about the appropriate input signal for testing the amplitude linearity of a single-sideband phone transmitter. The correct answer is C. Two audio-frequency sine waves. This method involves feeding two distinct audio sine waves into the transmitter and observing the output on an oscilloscope. The combination of these two tones allows for the assessment of how linearly the transmitter processes and combines multiple frequencies. It’s akin to playing two distinct notes on a piano and listening for any distortion or irregularities. The absence of such distortions on the oscilloscope display indicates good linearity, which is crucial for maintaining the quality and clarity of the transmitted signal.
Parallels:
- Harmony in Music: Like combining two notes to produce harmonious music, the two-tone test ensures that multiple frequencies are transmitted smoothly.
- Blending Colors: Similar to mixing two colors without muddying, this test ensures that multiple signals are combined cleanly.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- Two-Tone Input: Uses two separate audio frequencies for testing.
- Linearity Assessment: Evaluates how the transmitter combines these frequencies.
- Crucial for Signal Quality: Ensures clarity and fidelity in transmission.
- Oscilloscope Analysis: Visual representation of linearity is observed.
- Technical Standard in Transmitter Testing: Demonstrates a key aspect of transmitter quality control.
Frequency Selection in Two-Tone Test (A-005-004-007)
Two-Tone Test Frequency Selection: Question A-005-004-007 focuses on the specifics of a two-tone test for assessing the amplitude linearity of a single-sideband transmitter. The correct answer, B. Two non-harmonically related tones are fed in, and the output is observed on an oscilloscope, highlights the need for using two distinct audio tones that are not harmonically related. This choice ensures that any nonlinearities or distortions in the transmitter can be accurately detected and assessed. The use of an oscilloscope for this test provides a visual representation of how the transmitter processes these signals, revealing any anomalies or issues with linearity. The requirement for non-harmonic relation between the tones ensures that the test covers a broader range of potential distortions.
Parallels:
- Combining Different Ingredients: Like a chef combining diverse flavors to test a recipe, using non-harmonically related tones tests the transmitter’s ability to handle diverse signals.
- Testing Strength with Varied Weights: Similar to testing a structure’s strength with different weights, this test challenges the transmitter with varied audio signals.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- Non-Harmonic Tones: Ensures a comprehensive assessment of linearity.
- Oscilloscope Observation: Visual analysis of how signals are combined.
- Detects Nonlinearities: Identifies distortions and anomalies.
- Broad Range Testing: Covers various potential issues in signal processing.
- Essential for Maintaining Transmission Quality: A critical aspect of quality assurance in SSB transmitters.
Two-Tone Test in SSB Transmitter Linearity (A-005-004-008)
Audio Frequency Selection for Linearity Test: Question A-005-004-008 addresses the audio frequencies used in a two-tone test for assessing the linearity of a single-sideband phone transmitter. The correct answer, C. Any two audio tones may be used, but they must be within the transmitter audio passband, and should not be harmonically related, emphasizes the importance of selecting appropriate frequencies. These frequencies should be within the transmitter’s capable audio range and should not have a harmonic relationship to avoid interactions that could skew the test results. This test is akin to a stress test in machinery where different loads are applied to ensure robust performance under various conditions. The choice of non-harmonically related tones ensures that the transmitter’s response to a wide range of audio inputs is accurately assessed.
Parallels:
- Testing a Car’s Performance: Like testing a car with different types of terrain, this test challenges the transmitter with different audio frequencies to ensure robust performance.
- Musical Instrument Tuning: Similar to tuning a guitar with different notes, this test checks the transmitter’s ability to handle various audio frequencies accurately.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- Frequency Range and Selection: Must use frequencies within the transmitter’s audio passband and not harmonically related.
- Linearity Assessment: Evaluates the transmitter’s ability to process multiple frequencies simultaneously.
- Importance of Test Diversity: Ensures that the transmitter can handle a variety of audio inputs.
- Ensures Quality Transmission: Critical for maintaining the integrity of the transmitted signal.
- Technical Standard in RF Engineering: Reflects a comprehensive approach to transmitter testing.
Measuring Linearity in SSB Transmitters (A-005-004-009)
Linearity Evaluation Using Two-Tone Test: In Question A-005-004-009, the focus is on what can be measured in a single-sideband phone transmitter’s amplifier using a two-tone test and an oscilloscope. The answer, B. Its linearity, indicates that this test primarily assesses the transmitter’s linearity. By observing the combination of two audio-frequency tones on an oscilloscope, one can evaluate how linearly the transmitter combines and amplifies these signals. This is crucial to ensure that the transmitted signal maintains its integrity and quality without any distortions or nonlinearities. It’s similar to a sound engineer mixing multiple tracks to achieve a harmonious output; the two-tone test ensures the transmitter can blend different frequencies effectively and accurately.
Parallels:
- Blending Colors in Art: Just as an artist blends colors to create a new shade without distortion, the two-tone test ensures the transmitter blends frequencies without distortion.
- Testing a Recipe: Like testing a recipe with different ingredients, this test evaluates the transmitter’s ability to combine audio tones effectively.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- Evaluates Transmitter Linearity: Assesses how the transmitter combines multiple frequencies.
- Oscilloscope Usage: Provides a visual representation of the transmitter’s linearity.
- Essential for Signal Integrity: Ensures the transmitted signal is clear and undistorted.
- Standard Test in Transmitter Evaluation: A critical part of ensuring transmitter quality.
- Reflects Transmitter’s Performance: Indicates the transmitter’s capability to handle complex audio signals.
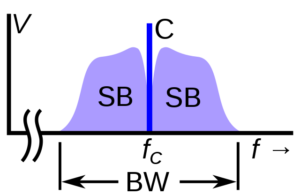
Carrier Suppression in SSB Transmission (A-005-004-010)
Carrier Suppression Level in SSB: Question A-005-004-010 explores the extent of carrier suppression in a single-sideband phone transmission. The correct answer, A. At least 40 dB, signifies the minimum level of carrier suppression typically achieved in SSB transmission. This high level of suppression is important to ensure that most of the transmitter’s power is efficiently used for transmitting the sideband information, which carries the actual communication content. Effective carrier suppression not only improves power efficiency but also reduces the potential for interference, making the transmission more focused and clear. It’s like turning off a bright background light to better see a specific object in the foreground, highlighting the desired information more effectively.
Parallels:
- Dimming Unnecessary Lights in a Room: Just as dimming lights not needed for a task can help focus attention, suppressing the carrier in SSB highlights the important sideband information.
- Reducing Background Noise: Similar to lowering background noise to hear a conversation clearly, carrier suppression in SSB ensures the clarity of the transmitted message.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- High-Level Carrier Suppression: At least 40 dB below peak output power.
- Improves Power Efficiency: Ensures efficient use of transmitter power.
- Reduces Interference: Minimizes potential for signal interference.
- Focuses on Sideband Information: Highlights the importance of sideband content in SSB.
- Key Aspect of SSB Transmission: Demonstrates the technical precision required in SSB technology.
“Flat-Topping” in SSB Transmission (A-005-004-011)
Understanding “Flat-Topping” in SSB: Question A-005-004-011 addresses the phenomenon of “flat-topping” in single-sideband phone transmission. The correct answer, A. Signal distortion caused by excessive drive, points to a common issue where the signal becomes distorted due to overdriving the amplifier. “Flat-topping” occurs when the peaks of the modulated signal are clipped or flattened, resulting in distortion and a potential increase in unwanted emissions. It’s akin to overfilling a container until the liquid spills over the edges, indicating an excess beyond the container’s capacity. In SSB transmission, avoiding “flat-topping” is crucial for maintaining signal integrity and preventing the generation of spurious emissions that can interfere with other communications.
Parallels:
- Overfilling a Glass: Similar to how overfilling a glass causes spillage, overdriving an SSB transmitter leads to signal distortion.
- Turning Up Volume Too High: Like distortion from a speaker when the volume is too high, “flat-topping” distorts the transmitted signal in SSB.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- Caused by Excessive Drive: Occurs when the amplifier is overdriven.
- Results in Signal Distortion: Leads to clipping of the signal’s peaks.
- Avoidance is Crucial: Important for maintaining clean transmission.
- Can Increase Unwanted Emissions: Potentially leads to interference with other signals.
- Reflects on Transmitter Management: Indicates the need for careful control of transmission levels.
Insights into AM and SSB Transmission Technologies
Throughout this chapter, we’ve navigated the technical landscape of AM and SSB transmitters, uncovering the intricacies behind their operation and performance. Key topics included the role of balanced modulators in creating double sideband, suppressed carrier signals, and the steps involved in producing clean and efficient single-sideband signals. The chapter highlighted the critical importance of carrier suppression in SSB transmissions, enhancing both power efficiency and signal clarity. We delved into the significance of linearity in transmitters, particularly for SSB, where fidelity and quality of the transmitted signal are crucial. The two-tone test emerged as an essential tool for evaluating this linearity, ensuring that transmitters can handle complex audio inputs without distortion. Additionally, the concept of “flat-topping” was discussed, emphasizing the need for careful modulation levels to maintain signal integrity. Overall, this chapter provided a thorough understanding of the technical considerations and best practices in AM and SSB transmitter design and operation, offering valuable insights for anyone interested in the field of RF communications.
© Hamshack.ca. All lesson content, diagrams, and quizzes are proprietary and protected by copyright. Access is for personal use only and requires a valid course purchase where applicable. Copying, sharing, or redistributing any material is strictly prohibited. Embedded third-party videos are provided for educational reference only and remain the property of their respective creators and platforms.
See the Hamshack.ca Terms of Use for full details.
