
Start Here
Advanced Components Practice Exam Overview
The Advanced Components Practice Exam is a crucial component of the preparatory path for those aiming to achieve the Advanced Amateur Radio certification, particularly targeting the Spectrum Management and Telecommunications Advanced Amateur Radio Exam. This specialized exam draws from a comprehensive pool of questions, encompassing all 12 courses dedicated to the advanced aspects of amateur radio technology and operations. Each attempt at the exam presents a unique set of 25 questions, randomly selected from a total pool of questions that thoroughly cover the following key areas:
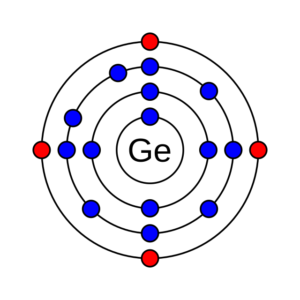
- Semiconductor Materials and Doping: This section tests the candidate’s understanding of the properties and doping processes of materials like Germanium, Silicon, and Gallium Arsenide to create P-type and N-type semiconductors.
- Diodes: Questions focus on various diode types, including point-contact, junction, hot-carrier, and Zener diodes, along with their specific applications in radio communications.
- Transistors: This area evaluates knowledge on the operation and application of NPN and PNP transistors in amplification and switching.
- Field-Effect Transistors (FETs): Candidates are tested on their understanding of JFETs and MOSFETs, their characteristics, and their roles in radio systems.
- Silicon-Controlled Rectifiers (SCRs): This section assesses the candidate’s grasp of SCRs and their utility in circuit power control.
- Amplifiers: Knowledge on the different classes of amplifiers (A, AB, B, C) and their application in radio communications is evaluated.
- Amplifier Circuits: The exam differentiates between discrete and integrated circuit amplifiers, focusing on their uses.
- Operational Amplifiers: Questions cover the properties and applications of operational amplifiers in amateur radio.
- Mixers and Frequency Multipliers: Understanding of the role of mixers and frequency multipliers in signal processing is tested.
- Digital Logic Elements: This section checks the candidate’s basic knowledge of digital logic and its applications in radio communications.
- Quartz Crystals: The exam explores the properties and applications of quartz crystals, especially in frequency stabilization.
- Advanced Filter Circuits: Knowledge of AF and RF filter circuits and their significance in signal processing is assessed.
The dynamic nature of the exam, with its 25 questions randomly selected for each attempt, ensures a comprehensive testing experience, encouraging candidates to achieve a deep and broad understanding of advanced amateur radio components and theories. This approach not only prepares candidates for the certification exam but also enhances their practical knowledge and skills in amateur radio operations.
Be sure to login to your hamshack.ca account to track your progress by clicking the [Mark Complete] Button at the bottom of each lesson. You can contact VE7DXE to sign-up for the new Basic Amateur course.
Well done on finishing the Advanced Components Practice Exam from the hamshack.ca QSL Advanced Amateur Radio course. This exam, with its 25 questions pulled from a large pool covering all 12 topics, was a critical step in testing your knowledge in advanced amateur radio components and theories.
Your success in this exam shows you’ve got a strong grasp of key areas like semiconductor materials, diodes, transistors, amplifiers, and more. These are essential for anyone looking to excel in the Advanced Amateur Radio certification and practical amateur radio operations.
Now that you’ve proven your skills in this area, it’s important to move on and complete the rest of the QSL Advanced Amateur Radio course material. This will prepare you fully for the Spectrum Management and Telecommunications Advanced Amateur Radio Exam. Keep focused, and use this exam as a stepping stone towards mastering the complete course content.
Keep it up, and good luck with the rest of your studies and the upcoming certification exam!
73 Don VE7DXE
© Hamshack.ca. All lesson content, diagrams, and quizzes are proprietary and protected by copyright. Access is for personal use only and requires a valid course purchase where applicable. Copying, sharing, or redistributing any material is strictly prohibited. See the Hamshack.ca Terms of Use for full details.
