Ham Radio License Canada – Hamshack
Online ISED Basic Course – Study from Home at Your Own Pace
How to Get a Ham Radio License in Canada?
If you are searching for how to get your ham radio license in Canada, you are looking to earn what is officially called the Amateur Radio Operator Certificate, issued by Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada (ISED). To legally operate amateur radio equipment in Canada, you must pass the ISED Basic Amateur Radio Certification exam and obtain your callsign.
The QSL Academy Online ISED Basic Ham Radio Course is structured directly around the official Canadian Amateur Radio Basic Question Bank. It prepares students to pass the Canadian amateur radio exam with confidence by covering regulations, operating procedures, station assembly and safety, electronics theory, antennas, propagation, and interference control.
This course is designed specifically for Canadians who want a clear, structured, and reliable path to earning their ham radio certification.
“Whether you are a complete beginner or preparing for the Canadian Amateur Radio Basic exam for the first time, this online course provides everything required to pass and receive your official ISED-issued callsign.”

From your first lesson to passing the official ISED Basic examination and receiving your Canadian amateur radio callsign, this structured pathway guides you step by step toward earning your Amateur Radio Operator Certificate.

Enroll Online
Register for the QSL Academy Canadian Amateur Radio Basic Course, updated to the latest official ISED Basic Question Bank and designed specifically to prepare you to pass the Canadian Amateur Radio Basic exam and earn your Amateur Radio Operator Certificate.
Study online anytime, anywhere with the structured ISED Basic Ham Radio Course in Canada, built to help you confidently obtain your ham radio license in Canada without attending time-consuming in-person classes. Learn at your own pace and prepare effectively for your official ISED examination.
This structured approach ensures you are fully prepared to pass the ISED Basic exam and confidently earn your Canadian Amateur Radio Operator Certificate.

Work through the basic course lessons
The QSL Academy Basic Course is fully self-contained — no additional textbooks, fixed schedules, or classroom attendance required. Every lesson is structured directly around the official ISED Basic Question Bank, ensuring you study exactly what is required to pass the Canadian Amateur Radio Basic exam and earn your Amateur Radio Operator Certificate.
The lesson content is carefully organized to help you understand regulations, operating procedures, electronics theory, antennas, propagation, and interference control — all essential topics needed to obtain your ham radio license in Canada. Each lesson concludes with a QSL Essentials Summary Table that clearly reinforces the key concepts required for exam success.
“This structured approach eliminates guesswork and focuses only on the material tested on the official ISED Basic examination.”

Complete Lesson Quizzes
Each lesson concludes with an interactive quiz designed to prepare you for the official ISED Basic Amateur Radio examination. These quizzes reinforce the material covered in the Canadian Amateur Radio Basic Course and help ensure you are fully prepared to pass the exam and earn your Amateur Radio Operator Certificate.
Every lesson also includes a QSL Essentials Summary Table that clearly highlights the key concepts, formulas, operating procedures, and regulations required to obtain your ham radio license in Canada. This structured approach ensures you master the material tested on the official ISED Basic exam before progressing to the next lesson.
“By the time you complete all lesson quizzes, you will be fully prepared to confidently write the Canadian Amateur Radio Basic exam.”

Complete Section Quizzes – Reinforce What You’ve Learned
Section quizzes combine all lesson material within each major subject area of the Canadian Amateur Radio Basic Course, giving you a comprehensive review before advancing. This structured format ensures you fully understand regulations, operating procedures, electronics, antennas, and propagation before progressing toward the official ISED Basic Amateur Radio examination.
Each section quiz is aligned directly with the official ISED Basic Question Bank, helping you strengthen comprehension, identify weak areas, and build the confidence required to pass the exam and earn your Amateur Radio Operator Certificate. By completing section quizzes, you move one step closer to obtaining your ham radio license in Canada and successfully writing the full 100-question Basic Amateur Radio exam.
“This progressive structure mirrors the format of the official Canadian Amateur Radio Basic examination, ensuring you are fully prepared before booking your exam.”

Complete the Practice Exam
After finishing all sections, take the full 100-question Practice Exam, structured to mirror the official ISED Basic Amateur Radio examination in format, difficulty, and subject distribution. All lesson quizzes, section quizzes, and the full practice exam are built directly from the official ISED Basic Question Bank — the same publicly released question pool used nationwide for the Canadian Amateur Radio Basic examination.
This comprehensive exam prepares you for the real Canadian Amateur Radio Basic exam and strengthens your readiness to earn your Amateur Radio Operator Certificate. The practice exam may be repeated as often as needed, and students receive a detailed report highlighting areas for review and improvement before attempting the exam again.
You are encouraged to continue practicing until you consistently achieve a score of 80% or higher. Reaching 80% positions you for Basic with Honours, which grants expanded operating privileges, including access to HF bands for long-distance (DX) communication. Preparing to consistently score 80% or higher ensures you are fully prepared to obtain your ham radio license in Canada at the highest available Basic certification level — with confidence and no surprises on exam day.
By the time you consistently score 80% or higher, you are fully prepared to write the official ISED Basic examination and confidently earn your Canadian Amateur Radio Operator Certificate.

Schedule and Complete the Official ISED Exam
To simplify the final step toward earning your ham radio license in Canada, Hamshack.ca works directly with Gary Skett, VE7AS — an Accredited Examiner authorized by Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada (ISED). Students may contact Gary to schedule the official ISED Basic Amateur Radio examination, which can be completed online for a nominal fee.
Upon successfully passing the exam, you will receive your Amateur Radio Operator Certificate, and your Canadian amateur radio callsign will be issued through the ISED licensing system. This streamlined process makes obtaining your Canadian amateur radio certification straightforward, accessible, and fully aligned with national licensing requirements.
“Gary Skett VE7AS has extensive experience administering the Canadian Amateur Radio Basic examination and guiding new operators through the certification process.”

Get your callsign and start operating!
After successfully completing the official ISED Basic Amateur Radio examination, students who pass the exam receive their Canadian amateur radio callsign directly during the online session with Gary Skett, VE7AS — an Accredited Examiner authorized by Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada (ISED).
Once your exam is marked as a pass, your callsign is issued and you are officially granted your Amateur Radio Operator Certificate, giving you your ham radio license in Canada. There is no waiting period — you are authorized to begin operating immediately within the privileges of your certification level.
“This means you can complete your exam and be on the air legally with your own Canadian callsign the same day.”


Has Radio Theory Been Holding You Back from Getting Certified?
Struggling with Ohm’s Law? Do formulas make your head spin? Does electrical theory feel intimidating? You’re not alone. For many new hams, the electronics and theory portion of the ISED Basic Amateur Radio examination can feel overwhelming at first.
That’s exactly why the QSL Tutor was built. Instead of forcing you to memorize formulas or guess your way through calculations, the Tutor works directly inside the Lesson Quizzes and Practice Exam — turning theory questions into guided learning experiences. Whether it’s Ohm’s Law, feedline loss, antenna length calculations, or basic circuit concepts, you receive clear, structured explanations that help you understand what the question is asking — without revealing the correct answer.
The result is simple: you actually understand the material. You learn how to break problems down step by step, apply the right formula, and arrive at the answer yourself. Instead of memorizing question patterns, you build real competence and walk into the ISED exam confident, capable, and in control.
The QSL Tutor is an AI-powered study tool developed by Don Rosberg VE7DXE specifically for Canadian amateur radio certification. Designed to support real learning without giving away answers, it makes preparing for your Amateur Radio Operator Certificate clearer, smarter, and more effective.
Recent Basic Course Graduates!




Built by a Canadian Operator, Designed for Canadian Students
Hamshack.ca has served the Canadian amateur radio community since 2020, facilitating thousands of equipment sales and supporting new operators across the country. The QSL Academy Basic Course was developed by Don Rosberg, VE7DXE, and is built on real-world amateur radio operating experience combined with extensive experience designing structured online learning systems that make technical concepts clear and accessible.
The course was created to provide a structured, affordable pathway into Canadian amateur radio certification — without the confusion often associated with traditional study materials.
Everything required to earn your Basic certification is included online. There are no extra textbooks to purchase, no rigid schedules, and no classroom commitments — helping students save up to $100 compared to many traditional in-person courses.
Students progress at their own pace, confirming comprehension through lesson quizzes and section exams before attempting the full Practice Exam. When practice scores consistently reach 80% or higher, students are ready to schedule their official ISED Basic Amateur Radio examination.
To simplify the final step, Hamshack.ca works directly with Gary Skett, VE7AS — an Accredited Examiner authorized by Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada (ISED). Students may arrange their online Basic examination for a nominal fee of $20, making the path from enrollment to callsign clear, straightforward, and accessible.
Frequently Asked Questions...
How do I get my Amateur Radio Operator Certificate in Canada?
To earn your Amateur Radio Operator Certificate in Canada, you must successfully pass the ISED Basic examination administered under Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada (ISED). Preparation requires understanding knowledge areas covered on the official ISED Basic examination, including Regulations and Policies, Operating and Procedures, Station Assembly, Practice and Safety, Circuit Components, Basic Electronics and Theory, Feedlines and Antenna Systems, Radio Wave Propagation, and Interference and Suppression.
The QSL Academy Amateur Radio Basic Course provides a structured pathway designed specifically to prepare students for the ISED Basic examination. Built directly around the latest official question bank, the course guides students through organized lessons, integrated quizzes, section reviews, and full-length practice exams before scheduling the official exam on-line. You get to select your ham radio callsign after passing the Basic exam, so there’s no waiting to get on the air and start enjoying ham radio in Canada and worldwide!
How much does the QSL Academy Basic Course cost?
The QSL Academy Basic Course is priced at $39 CAD, providing full access to the complete online course. This fee includes everything you need to pass your amateur radio basic certification in Canada. You’ll access easy to use structured lessons built around the latest official ISED Basic Question Bank, integrated quizzes, comprehensive section reviews, and full-length practice exams to ensure you’re prepared for the ISED Basic amateur radio exam.
There are no additional textbooks to purchase, no supplementary materials required, and no extra fees for course access. The $39 enrollment fee includes everything you need to pass the Basic Amateur Radio exam and get your Canadian Amateur Radio Basic Operator Certificate.
Will I have to study a lot of material that isn’t on the exam?
No…the QSL Academy Canadian Amateur Radio Basic Course is designed to teach you exactly what is required to pass the ISED Basic Amateur Radio exam — nothing unnecessary and no unrelated material. Every lesson is aligned directly with the official ISED Basic Question Bank.
This focused approach eliminates information overload and keeps your preparation efficient and practical. You study what matters for certification, build real understanding of the required topics, and prepare confidently for the Canadian Amateur Radio Basic exam without wasting time on content that is not on the exam.
Can I complete my amateur radio certification entirely online?
Yes. Preparation for Canadian amateur radio certification can be completed fully online. The QSL Academy Basic Course provides immediate online access to structured lessons, quizzes, and practice exams, allowing students to study at their own pace from anywhere with an internet connection.
In addition, the official ISED Basic examination may be scheduled online with an Accredited Examiner, creating a streamlined and accessible pathway from your first lesson to certification.
Do I need to purchase textbooks or additional study materials?
No additional textbooks are required when enrolling in the QSL Academy Basic Course. The course is fully self-contained and built directly around the latest official ISED Basic Question Bank.
All lessons, quizzes, and practice exams are included within the online platform, eliminating the need for separate study guides or classroom materials.
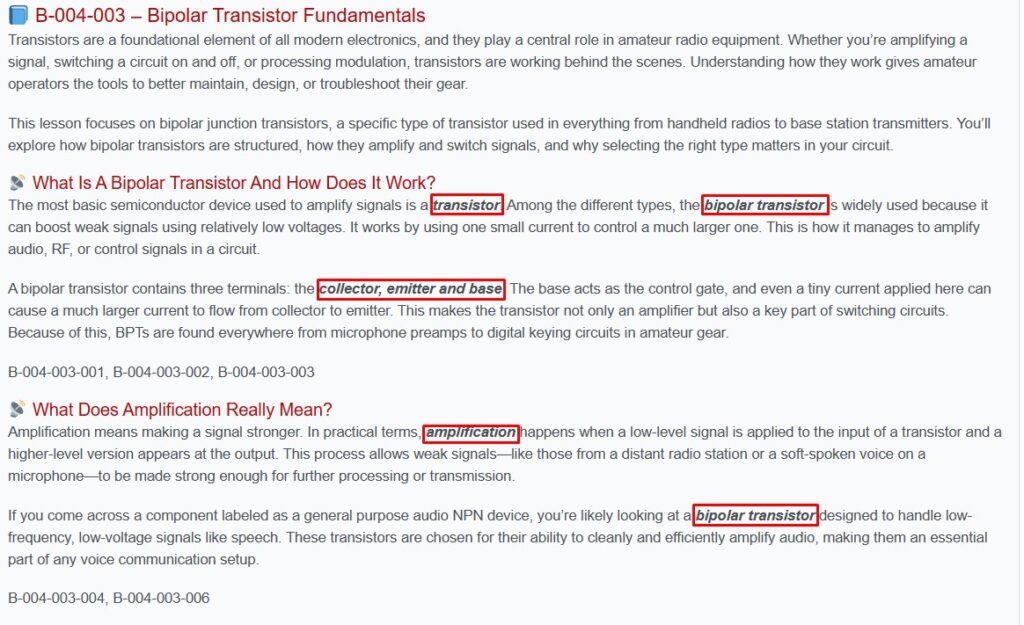
How are the lessons structured?
The QSL Academy Basic Course is structured around the latest official ISED Basic Question Bank, with each lesson organized to explain the concepts behind the exam questions in a clear and logical sequence. Rather than presenting isolated question-and-answer memorization, the course embeds the official ISED Basic exam answers directly within the instructional content so students understand why each answer is correct. This integrated approach improves retention, strengthens comprehension, and prepares students to confidently pass the ISED Basic exam.
How do the practice quizzes and exams work in the QSL Academy Basic Course?
The QSL Academy Canadian Amateur Radio Basic Course follows a clear progression: Lesson Quizzes, Section Quizzes, and finally full-length Practice Exams.
Students may repeat section quizzes and practice exams as needed. This step-by-step structure — lesson quiz, section quiz, final practice exam — provides a clear path toward readiness for the Canadian Amateur Radio Basic exam.

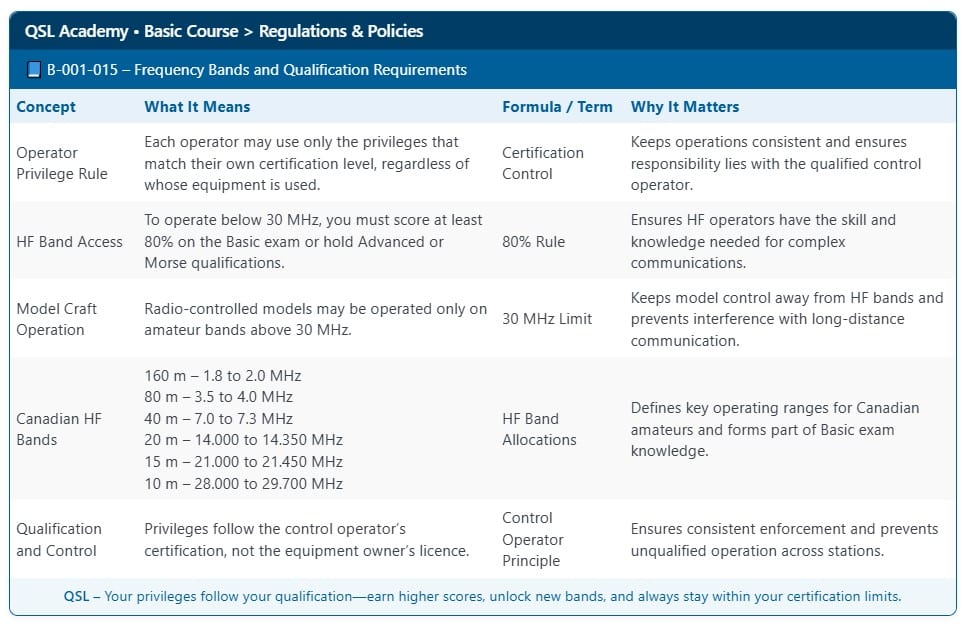
What are the QSL Essentials Tables, and how do they help with exam preparation?
The QSL Essentials Tables appear at the end of each lesson in the QSL Academy Canadian Amateur Radio Basic Course. They summarize the key concepts covered in that lesson in a clear, organized format to make review simple and efficient.
These structured summaries highlight the most important ideas from the official ISED Basic Question Bank, helping students quickly reinforce what they have just learned. By providing a focused recap at the end of each Lesson, the Tables support retention and make it easier to prepare for the ISED Basic Amateur Radio examination.
Amateur radio equipment seems confusing, does the course help explain it?
The QSL Academy Canadian Amateur Radio Basic Course includes practical equipment examples throughout the lessons, with images included from actual listings on hamshack.ca. The images help students recognize common ham radio transceivers, amplifiers and other station components while studying for the ISED Basic Amateur Radio examination.
The course makes it easier to connect theory with what students will eventually see and use, by including images from the ham radio buy and sell listings. The primary goal remains clear preparation for the Canadian Amateur Radio Basic exam, while providing just enough practical reference to support understanding before earning an Amateur Radio Operator Certificate in Canada.






