Start Here
Receiver Components and Functions
Welcome to the chapter on “Detection, Audio, Automatic Gain Controls.” This section is designed to deepen the understanding of crucial components and mechanisms within modern communication receivers, particularly relevant in amateur radio. Over the course of this chapter, participants will explore intricate aspects of receiver technology, covering topics such as the role of de-emphasis networks in FM receivers, the functionality of product detectors, and the dynamics of Automatic Gain Control (AGC) systems. Key questions will guide learners through the nuances of signal processing, from detection to audio output, and the critical role of AGC in maintaining consistent signal quality. This journey through receiver technology will provide insights into how receivers manage varying signal strengths, demodulate complex signal types, and ensure clear audio reproduction. The knowledge gained here is essential for anyone interested in the technical aspects of radio communication, offering valuable skills for both amateur radio enthusiasts and professionals in the field.
A-006-004-001: What audio shaping network is added at an FM receiver to restore proportionally attenuated lower audio frequencies?
De-Emphasis Network in FM Receivers (A-006-004-001)
Restoring Lower Audio Frequencies in FM Receivers
Question (A-006-004-001) addresses the use of a de-emphasis network in FM receivers. The correct answer, B. A de-emphasis network, is crucial for restoring proportionally attenuated lower audio frequencies. In FM transmission, higher audio frequencies are often emphasized (pre-emphasized) to improve the signal-to-noise ratio and reduce the impact of high-frequency noise. This emphasis leads to a disproportionate increase in the level of these frequencies, potentially skewing the audio quality.
The de-emphasis network in the receiver performs the inverse function of pre-emphasis. It attenuates the higher frequencies to their original level, ensuring a balanced and natural frequency response in the audio output. This network typically consists of a simple RC (resistor-capacitor) circuit, which acts as a low-pass filter, reducing the level of high frequencies and thus compensating for the pre-emphasis applied at the transmitter.
The implementation of de-emphasis is essential for maintaining the fidelity of audio broadcasts in FM radio. Without it, the audio would sound unnaturally bright and potentially fatiguing to the listener. The de-emphasis network ensures that the final audio output closely matches the original sound, providing listeners with a clear and pleasant listening experience.
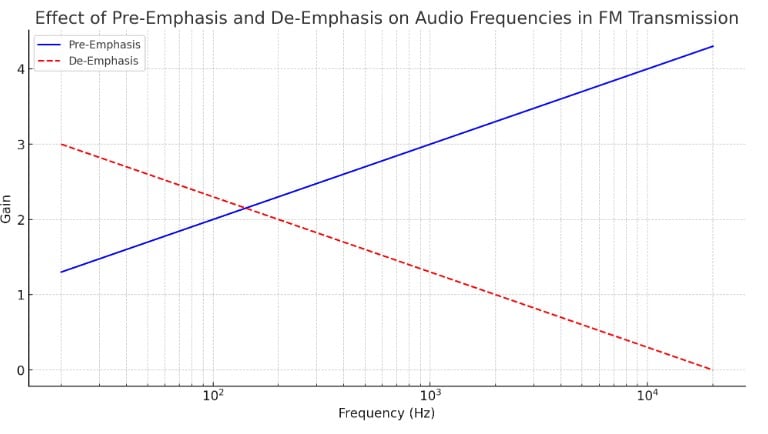
The graph illustrates the effects of pre-emphasis and de-emphasis on audio frequencies in FM transmission:
- The Pre-Emphasis curve (blue) shows how higher audio frequencies are amplified before transmission. This emphasis improves the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) for these frequencies, making the transmitted signal less susceptible to high-frequency noise.
- The De-Emphasis curve (red dashed line) demonstrates the counteractive measure taken at the receiver. It proportionally attenuates the higher frequencies that were previously emphasized, aiming to restore the original audio signal’s frequency balance. This ensures that the audio quality is maintained and not skewed by the pre-emphasis process.
By employing both pre-emphasis at the transmitter and de-emphasis at the receiver, FM transmission systems can effectively enhance signal quality while preserving the fidelity of the original audio content.
Parallels:
- Color Balancing in Photography: Adjusting color balance in photos to reflect true colors is similar to how the de-emphasis network restores natural audio frequency response.
- Adjusting Glasses for Clear Vision: Just as glasses correct vision to see the world as it is, the de-emphasis network adjusts audio frequencies for accurate sound reproduction.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- Role of De-Emphasis Network: It restores lower frequencies attenuated during FM transmission.
- Counteracts Pre-Emphasis: De-emphasis is the inverse process of pre-emphasis applied at the transmission stage.
- Ensures Balanced Audio Output: Crucial for maintaining natural sound quality in FM broadcasting.
- Function as a Low-Pass Filter: The network typically uses an RC circuit to achieve its purpose.
- Improves Listener Experience: Essential for delivering clear and pleasant audio to FM radio listeners.
A-006-004-002: What does a product detector do?
Product Detector Function (A-006-004-002)
Role of a Product Detector in Signal Processing
Question (A-006-004-002) examines the purpose of a product detector in a receiver. The correct answer, A. It mixes an incoming signal with a locally generated carrier, highlights the product detector’s essential role in demodulating certain types of signals. The product detector is particularly crucial in modes like Single Sideband (SSB) and Continuous Wave (CW), where it mixes the incoming modulated signal with a signal from a beat-frequency oscillator (BFO). This mixing process effectively extracts the audio component from the modulated carrier, allowing for the recovery and audible representation of the transmitted information.
The product detector’s operation is based on the principle of heterodyning, where two frequencies are mixed to produce sum and difference frequencies. In the context of SSB or CW signals, the product detector uses this principle to isolate the audio frequency from the complex waveforms received. This process is key to ensuring that voice or Morse code signals are intelligible to the listener.
In amateur radio, the product detector’s ability to accurately demodulate signals without introducing significant distortion is vital for effective communication. Its performance can significantly impact the clarity of received transmissions, making it a critical component in the design of receivers used in these modes.
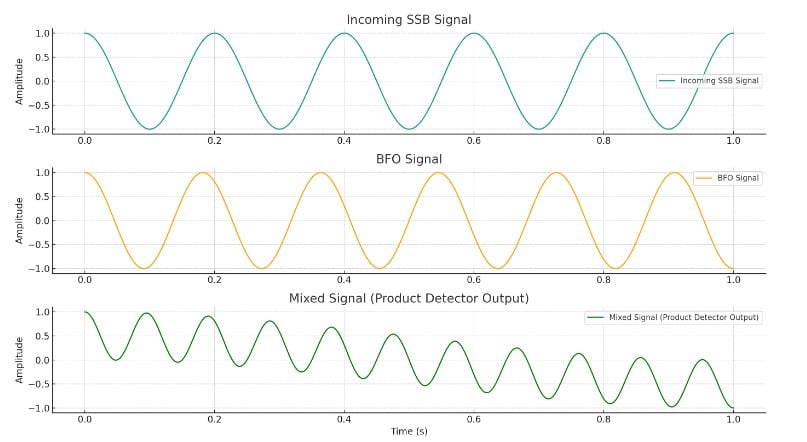
Parallels:
- Extracting Flavor in Cooking: Like extracting the essential flavors from a mixture of ingredients, the product detector isolates the audio from the carrier signal.
- Separating Vocals in Music Production: Similar to isolating the vocal track from a complex musical composition, the product detector extracts the intelligible audio signal from the modulated waveform.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- Function of Product Detector: Mixes incoming signal with a BFO signal to demodulate SSB and CW modes.
- Based on Heterodyning Principle: Utilizes sum and difference frequencies to isolate audio.
- Critical for SSB/CW Reception: Ensures clear and intelligible voice or Morse code signals.
- Impact on Signal Clarity: Plays a key role in the quality of received transmissions in amateur radio.
- Essential Component in Receivers: A vital part of receiver design for accurate signal demodulation.
A-006-004-003: Distortion in a receiver that only affects strong signals usually indicates a defect in or misadjustment of the:
Automatic Gain Control in Strong Signals (A-006-004-003)
AGC’s Role in Handling Strong Signals
Question (A-006-004-003) focuses on the effect of distortion in a receiver that primarily affects strong signals. The correct answer, D. automatic gain control (AGC), points to the AGC as a potential source of this issue. In a receiver, the AGC is responsible for automatically adjusting the gain to maintain a consistent output level despite varying signal strengths. When functioning correctly, the AGC prevents strong signals from overloading the receiver, which can cause distortion.
However, if there’s a defect or misadjustment in the AGC circuit, it may fail to properly reduce the gain for strong signals, leading to their distortion. The AGC works by measuring the strength of the incoming signal and then adjusting the gain of the RF and IF amplifier stages accordingly. A well-adjusted AGC ensures that all signals, whether weak or strong, are processed at an optimal level, providing a clear and distortion-free output.
For amateur radio operators, understanding the AGC’s function is vital, especially when operating in environments with a wide range of signal strengths. An improperly functioning AGC can significantly affect the quality of received signals, making it a critical aspect of receiver performance to monitor and maintain.
Parallels:
- Volume Control in Audio Systems: The AGC’s role in a receiver is like an automatic volume control in an audio system, adjusting the loudness to prevent distortion.
- Traffic Flow Regulation: Similar to how traffic lights regulate the flow of vehicles to prevent congestion, the AGC adjusts gain to prevent signal overload.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- AGC Prevents Overload: Automatically adjusts gain to maintain consistent output levels.
- Critical for Strong Signal Handling: Protects against distortion caused by strong signals.
- Adjustment is Key: Misadjustment can lead to poor performance and signal distortion.
- Vital for Clear Reception: Essential for ensuring quality reception across varying signal strengths.
- Important for Amateur Radio: Understanding and maintaining AGC is crucial in amateur radio setups
A-006-004-004: In a superheterodyne receiver with automatic gain control (AGC), as the strength of the signal increases, the AGC:
AGC Function in Superheterodyne Receivers (A-006-004-004)
Automatic Gain Control Response to Signal Strength
Question (A-006-004-004) inquires about the function of automatic gain control (AGC) in a superheterodyne receiver as the strength of the signal increases. The correct answer, C. Reduces the receiver gain, explains how AGC works to maintain a consistent audio output level. As the strength of the incoming signal increases, the AGC circuitry automatically reduces the gain of the receiver to prevent overloading and distortion. This feature is particularly important for ensuring that strong signals do not overpower the receiver’s circuitry, which can result in poor audio quality or even damage to the receiver.
The AGC operates by measuring the strength of the incoming signal and then dynamically adjusting the amplification applied by the RF and IF stages. This mechanism ensures a stable output volume, regardless of fluctuations in signal strength, making it a vital component in high-quality radio receivers. For amateur radio enthusiasts, a well-functioning AGC system is essential for comfortable listening and effective communication, especially when dealing with signals of varying intensities.
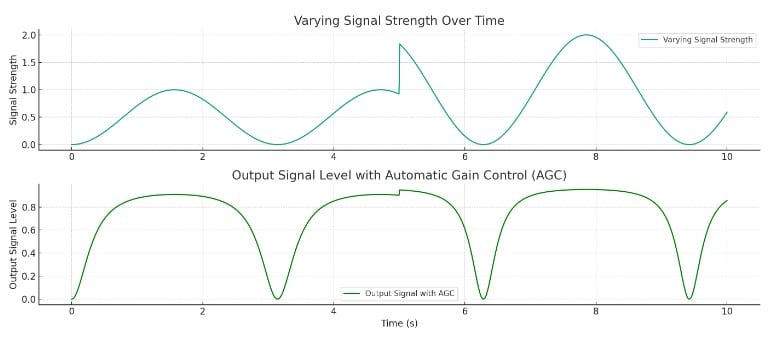
The graph visualizes the function of Automatic Gain Control (AGC) in a receiver, showcasing how it manages to maintain a consistent output level despite variations in incoming signal strengths:
- Varying Signal Strength Over Time: The first plot demonstrates how the signal strength varies over time, with an increase in strength observed in the second half of the time period. This variation could potentially lead to issues such as receiver overload and distortion without proper gain control.
- Output Signal Level with Automatic Gain Control (AGC): The second plot illustrates the output signal level after the AGC has adjusted the gain. Despite the fluctuations in the incoming signal strength, the AGC successfully maintains a relatively consistent output level. By automatically adjusting the gain inversely proportional to the incoming signal strength, the AGC prevents the receiver from being overloaded by strong signals, thereby avoiding distortion and ensuring a stable and clear reception.
This demonstrates the critical role of AGC in radio receivers, allowing them to handle a wide range of signal strengths effectively and ensuring optimal performance across varying reception conditions.
Parallels:
- Thermostat Regulating Temperature: The AGC in a receiver is akin to a thermostat in a room, automatically adjusting to maintain a consistent temperature.
- Cruise Control in Vehicles: Similar to how cruise control adjusts a vehicle’s speed based on road conditions, AGC adjusts gain based on signal strength.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- AGC Adjusts to Signal Strength: Reduces gain as signal strength increases to prevent overloading.
- Prevents Audio Distortion: Essential for maintaining audio quality with strong signals.
- Dynamic Amplification Adjustment: Continuously adjusts amplification levels for stability.
- Critical for Receiver Integrity: Protects the receiver from being overwhelmed by strong signals.
- Important for Amateur Radio Use: Ensures effective communication across a range of signal conditions.
A-006-004-005: The amplified IF signal is applied to the stage in a superheterodyne receiver.
IF Signal Application in Receivers (A-006-004-005)
Detecting the Amplified IF Signal
Question (A-006-004-005) asks about the stage in a superheterodyne receiver where the amplified IF signal is applied. The correct answer, C. Detector, identifies the stage responsible for converting the IF signal into an audio signal. The detector stage plays a pivotal role in the final signal processing within the receiver. After the IF signal is sufficiently amplified, it is fed into the detector, which demodulates the signal, extracting the original audio or
data information.
This stage is crucial as it translates the complex modulated waveforms into a form that can be understood or heard by the user. The detector’s effectiveness directly impacts the clarity and fidelity of the received signal. In superheterodyne receivers, this stage ensures that the signal, after undergoing various amplification and filtration processes, is finally rendered into an intelligible output, be it voice, music, or digital data.
For amateur radio operators and enthusiasts, understanding the function of the detector stage is vital. It is the final step in the intricate process of receiving and processing radio signals, and its efficiency determines the overall quality of the received transmission.
Parallels:
- Deciphering Code in Cryptography: The detector’s role in demodulating signals is like deciphering a coded message, revealing the underlying information.
- Translating a Foreign Language: Similar to how a translator converts a foreign language into a familiar one, the detector translates modulated signals into audio or data.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- Detector Demodulates IF Signal: Converts the IF signal into an audio or data format.
- Final Stage in Signal Processing: Last step in transforming received radio signals into understandable forms.
- Impacts Signal Clarity: The efficiency of the detector directly affects the quality of the output.
- Key Component in Receivers: Essential for ensuring the intelligibility of received transmissions.
- Crucial for Amateur Radio: Understanding its function is important for radio communication and troubleshooting.
A-006-004-006: The low-level output of a detector is:
Amplification of Detector’s Low-Level Output (A-006-004-006)
Handling Detector’s Low-Level Output in Receivers
Question (A-006-004-006) explores what happens to the low-level output of a detector in a receiver. The correct answer, B. Applied to the AF amplifier, indicates that this weak signal is sent to the audio frequency (AF) amplifier for further amplification. The detector’s output is typically at a low level and needs additional amplification to be audible through speakers or headphones.
The AF amplifier plays a crucial role in boosting this low-level audio signal to a level that can be comfortably heard by the user. This stage is designed to amplify the signal without introducing significant distortion, ensuring that the audio remains clear and true to the original transmission. In the context of amateur radio, the AF amplifier’s performance is key to a satisfying listening experience, particularly when receiving weak or distant signals.
Parallels:
- Microphone Amplification in PA Systems: Similar to how a microphone’s weak output is amplified in a public address system, the detector’s output is boosted by the AF amplifier.
- Magnifying a Small Object: Like using a magnifying glass to enlarge a small object for better visibility, the AF amplifier enlarges the audio signal for better audibility.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- Amplification of Detector Output: The AF amplifier boosts the detector’s low-level output.
- Essential for Audio Clarity: Ensures the audio signal is loud enough without distortion.
- Crucial Stage in Audio Output: Integral to converting the detected signal into a usable form.
- Importance in Weak Signal Reception: Particularly vital for clear audio in weak signal scenarios.
- Key for Amateur Radio Equipment: Understanding its role helps in evaluating and troubleshooting receiver performance.
A-006-004-007: The overall output of an AM/CW/SSB receiver can be adjusted by means of manual controls on the receiver or by use of a circuit known as:
Manual and Automatic Gain Control in Receivers (A-006-004-007)
Adjusting Receiver Output with AGC
Question (A-006-004-007) delves into how the overall output of an AM/CW/SSB receiver can be adjusted. The correct answer, A. Automatic gain control (AGC), points to a crucial circuit in receiver design. AGC automatically adjusts the receiver’s gain based on the signal strength, maintaining a consistent output level. This feature is especially important in environments with varying signal strengths, as it prevents strong signals from overwhelming the receiver and ensures weak signals are amplified sufficiently.
Manual controls on the receiver allow users to adjust the gain according to their preferences or specific reception conditions. The AGC, however, provides a more hands-off approach, automatically adapting to changing signal conditions. This automatic adjustment is vital for maintaining audio quality and preventing receiver overload, making AGC an indispensable feature in modern radio receivers.
Parallels:
- Auto-Brightness on Smartphones: AGC’s function is similar to the auto-brightness feature on smartphones, adjusting the screen brightness based on ambient light.
- Cruise Control in Vehicles: Like cruise control maintaining a car’s speed, AGC maintains the receiver’s gain at an optimal level.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- Function of AGC: Automatically adjusts the gain in response to changing signal strengths.
- Maintains Consistent Output: Helps keep the audio output stable despite variations in signal strength.
- Prevents Overload and Distortion: Essential for protecting the receiver from strong signal overload.
- Enhances Listening Experience: Ensures audio quality is maintained across different reception conditions.
- Manual Control Option: Users can also adjust gain manually for specific needs.
A-006-004-008: AGC voltage is applied to the:
Application of AGC Voltage (A-006-004-008)
AGC Voltage Influence in Receivers
Question (A-006-004-008) asks where the AGC voltage is applied in a receiver. The correct answer, A. RF and IF amplifiers, indicates that AGC voltage primarily affects these two critical stages. AGC voltage is used to regulate the gain of both the RF (Radio Frequency) and IF (Intermediate Frequency) amplifiers in response to the strength of the incoming signal. By adjusting the gain of these stages, the AGC helps maintain a consistent signal level for processing and output, regardless of the variations in signal strength.
This regulation is crucial for achieving a balanced performance, especially when receiving signals of differing intensities. It ensures that weak signals are sufficiently amplified for clarity, while strong signals are attenuated to prevent distortion and receiver overload. In the context of amateur radio, where operators may encounter a wide range of signal conditions, the effective application of AGC voltage is key to versatile and reliable receiver performance.
Parallels:
- Adjusting Lights in a Theater: The way AGC voltage controls the amplifiers is akin to adjusting lighting for different scenes in a theater.
- Controlling Water Pressure: Similar to a valve controlling water pressure in a pipeline, AGC voltage regulates gain in the receiver.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- AGC Voltage on RF and IF Amplifiers: AGC voltage is applied to regulate the gain of these amplifiers.
- Responds to Signal Strength: Adjusts amplifier gain according to the intensity of the incoming signal.
- Balances Signal Processing: Ensures weak signals are amplified and strong signals are moderated.
- Prevents Overload and Distortion: Critical for maintaining signal integrity and quality.
- Key for Diverse Signal Environments: Especially important in amateur radio for handling various signal conditions.
A-006-004-009: AGC is derived in a receiver from one of two circuits. Depending on the method used, it is called:
Sources of AGC in Receivers (A-006-004-009)
Deriving AGC in Communication Receivers
Question (A-006-004-009) explores the sources from which Automatic Gain Control (AGC) is derived in a receiver. The correct answer, B. IF derived or audio derived, indicates that AGC can be generated based on signal levels either at the Intermediate Frequency (IF) stage or from the audio output. IF-derived AGC is typically faster and more responsive to rapid signal strength changes, making it suitable for modes like AM or FM where signal strengths can fluctuate quickly. On the other hand, audio-derived AGC, which responds to the volume of the audio output, tends to be slower and is often used in communication modes like Single Sideband (SSB), where it can provide a more comfortable listening experience with less abrupt changes in volume.
Understanding the source of AGC is important for amateur radio operators as it affects how the receiver responds to varying signal conditions. This knowledge can guide users in choosing the right type of receiver for their specific needs, especially when operating in diverse signal environments.
Parallels:
- Sensing Light in Photography: Choosing between IF or audio-derived AGC is like a camera selecting between different light sensors for the best photo.
- Thermostat Settings: Similar to a thermostat using different sensors to control room temperature, AGC uses different sources to regulate gain.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- Two Sources of AGC: AGC can be derived from either the IF stage or the audio output.
- IF-Derived for Rapid Response: Suitable for modes with quick signal strength changes.
- Audio-Derived for Smoother Control: Used in modes like SSB for gradual volume adjustments.
- Impacts Receiver Responsiveness: The source of AGC affects how the receiver adapts to signal variations.
- Choice Based on Communication Mode: Operators can choose receivers based on the type of AGC that suits their mode of operation.
A-006-004-010: Which two variables primarily determine the behavior of an automatic gain control (AGC) loop?
Variables Determining AGC Behavior (A-006-004-010)
Influential Factors in AGC Performance
Question (A-006-004-010) asks about the primary variables that determine the behavior of an Automatic Gain Control (AGC) loop in a receiver. The correct answer, B. Threshold and decay time, points out two key factors influencing AGC performance. The threshold level sets the signal strength at which the AGC begins to reduce the gain, while the decay time determines how quickly the AGC responds to changes in signal strength.
The threshold ensures that the AGC only activates when needed, preventing unnecessary gain adjustments for weak signals. The decay time is crucial for managing how rapidly the receiver adapts to changes in signal strength, impacting the listening experience. A fast decay time can lead to abrupt changes in volume, while a slower decay time results in a more gradual adjustment, which can be more pleasant for the listener but might not be as effective in rapidly changing signal environments.
For amateur radio operations, understanding these variables is essential for optimizing receiver performance, especially when dealing with dynamic signal conditions. It allows operators to tailor their equipment for specific communication needs, ensuring clear and consistent reception.
Parallels:
- Adjusting Sensitivity in Security Systems: Like setting the sensitivity and response time of a security alarm, AGC’s threshold and decay time determine how it reacts to signal changes.
- Setting Reaction Time in Sports: Similar to an athlete adjusting reaction times for different events, AGC’s decay time adapts to signal strength variations.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- Threshold and Decay Time: Primary variables in AGC behavior.
- Threshold for Activation: Determines when AGC starts adjusting gain.
- Decay Time for Responsiveness: Affects how quickly AGC adapts to signal changes.
- Balancing AGC Settings: Key for tailored receiver performance in various signal environments.
- Crucial for Amateur Radio Use: Understanding these variables helps in effective communication setup.
A-006-004-011: What circuit combines signals from an IF amplifier stage and a beat-frequency oscillator (BFO), to produce an audio signal?
Product Detector in Receiver Circuitry (A-006-004-011)
Function of a Product Detector in Receivers
Question (A-006-004-011) explores the role of a product detector in a receiver. The correct answer, A. A product detector circuit, highlights its importance in combining signals from an IF amplifier stage and a beat-frequency oscillator (BFO) to produce an audio signal. The product detector is essential in modes like SSB and CW, where it demodulates the received signal by mixing it with a BFO signal. This process allows the conversion of the modulated IF signal back into an audio signal that can be heard or further processed.
In amateur radio receivers, the product detector is a critical component for effectively receiving and decoding SSB and CW signals. Its ability to accurately demodulate these signals is key to clear and intelligible communication. The product detector’s performance directly impacts the quality of the received audio, making it a focal point in receiver design for these specific communication modes.
Parallels:
- Blender Mixing Ingredients: Similar to a blender combining ingredients to create a smoothie, the product detector mixes IF and BFO signals to produce audio.
- Translator Converting Languages: Like a translator converting a foreign language into a familiar one, the product detector translates modulated signals into understandable audio.
Question Summary and Key Takeaways:
- Demodulates SSB and CW Signals: Essential for extracting audio from these specific signal types.
- Mixes IF and BFO Signals: Combines these signals to revert the modulated signal back into audio.
- Critical for Receiver Design: A key component in designing receivers for SSB and CW modes.
- Impacts Audio Quality: The effectiveness of the product detector influences the clarity of received communication.
- Essential in Amateur Radio: Understanding its function is crucial for operators using these modes.
Course Summary: Synthesizing Advanced Receiver Technologies
As we conclude the chapter on “Detection, Audio, Automatic Gain Controls,” learners have now acquired a detailed understanding of the sophisticated components and systems that comprise modern receivers. Throughout this chapter, participants have delved into the operational principles of various receiver elements, learning about the critical functions of product detectors, de-emphasis networks, and the intricacies of AGC. The exploration of how AGC adapts to signal strength changes, coupled with an understanding of how detectors and audio processing stages work, equips learners with comprehensive knowledge essential for effective radio communication.
This chapter has not only provided theoretical insights but also practical applications, particularly relevant to amateur radio operations. Understanding these receiver components allows for better equipment selection, setup, and troubleshooting, enhancing overall communication capabilities. As learners move forward in their radio communication journey, the knowledge gained here about detection, audio processing, and automatic gain control will serve as a foundation for mastering more complex aspects of receiver technology and signal processing.
