

Start Here
Gear up for the 8.1.3 Measurements Practice Exam, an essential segment of the hamshack.ca QSL Advanced Amateur Radio course material. This targeted exam assesses your proficiency in various measurement techniques and tools crucial for any advanced-level amateur radio operator. The exam encompasses a variety of topics, which include:
- AC Measurements: Knowledge of alternating current characteristics such as peak, peak-to-peak, average, and RMS values.
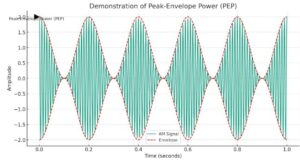
- Power Measurements: Understanding of Peak Envelope Power (PEP), comparisons of PEP to average power, and calculations related to the voltage across the load.
- Radio Testing Equipment: Familiarity with the use of dip meters and signal generators in radio tuning and testing.
- Calibration and Frequency Measurement: Proficiency with crystal calibrators, marking generators, and frequency counters for accurate signal processing.
- Oscilloscope: Skills in using an oscilloscope for visualizing waveforms and signal analysis.
- Meters and Measurement Devices: Competence in utilizing meters, multimeters, and power meters for various electrical and radio frequency measurements.
Structured with 25 questions selected from a comprehensive pool, the 8.1.3 Measurements Practice Exam is designed to test and reinforce your understanding of these measurement concepts and tools. It allows multiple attempts, ensuring you can measure your progress and achieve a deep understanding of the content.
Be sure to login to your hamshack.ca account to track your progress by clicking the [Mark Complete] Button at the bottom of each lesson. You can contact VE7DXE to sign-up for the new Basic Amateur course.
After completing the 8.1.3 Measurements Practice Exam, you’ve demonstrated your ability to navigate the technicalities of radio measurements, a vital skill set for advanced amateur radio operation. You’ve engaged with AC measurement techniques, understood the nuances of power measurement in radio systems, and gained hands-on knowledge about crucial radio testing equipment.
With this practice under your belt, you’re better equipped to handle the practical aspects of radio measurements and continue your preparation for the Spectrum Management and Telecommunications Advanced Amateur Radio Exam. The next step is to proceed with the rest of the hamshack.ca QSL Advanced Amateur Radio course material, armed with the confidence and understanding you’ve gained from this exam.
© Hamshack.ca. All lesson content, diagrams, and quizzes are proprietary and protected by copyright. Access is for personal use only and requires a valid course purchase where applicable. Copying, sharing, or redistributing any material is strictly prohibited. Embedded third-party videos are provided for educational reference only and remain the property of their respective creators and platforms.
See the Hamshack.ca Terms of Use for full details.
